Plenty was spent by Malaysian multinational timber tycoon Yii Ann Hii unsuccessfully fighting $A 64m in income tax. This tax litigation looks like it has just ended with Hii v Commissioner of Taxation (No 2) [2020] FCA 345 in March 2020.
The litigation
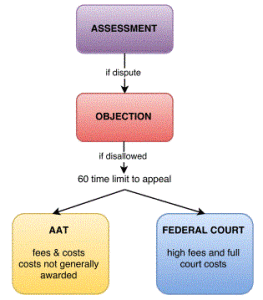
Although the litigation with the Commissioner of Taxation was about whether the taxpayer was a resident of Australia between 30 June 2001 to 30 June 2009 (the relevant years), this issue never came to be decided in the litigation with the Commissioner which included:
- a tax appeal to the Federal Court from objection decisions;
- an appeal to the Administrative Appeals Tribunal for administrative review in relation to penalty assessments for the relevant years;
- proceedings under section 39B of Judiciary Act 1903 collaterally taken in the Federal Court: Hii v Commissioner of Taxation [2015] FCA 375 before Collier J.;
- an original proceeding in the High Court under sub-section 75(5) of the Constitution seeking writs of certiorari and mandamus; and
- further proceedings under section 39B of Judiciary Act taken in the Federal Court seeking to quash an audit decision and an objection decision: Hii v Commissioner of Taxation (No 2) [2020] FCA 345 before Logan J.
An insight into the Australian tax system
Although the litigation never came to decide whether the Commissioner was correct in finding that the taxpayer was a resident taxable on worldwide income during the relevant years there is something to be drawn from these cases about the operation of Australia’s tax system.
Forum to fight the Commissioner
As we have said before on this blog in Is an objection needed to amend a tax assessment?, proceedings against the Commissioner other than under Part IVC (of the Taxation Administration Act 1953) where taxpayers can object against assessments of tax and appeal against the objection decisions arising, are expensive and are prone to failure. In Hii No. 1 Collier J. applied the High Court’s decision in Federal Commissioner of Taxation v Futuris Corporation Ltd (2008) 237 CLR 146 where it was held, by virtue of section 175 and section 177 of the Income Tax Assessment Act (ITAA) 1936, that judicial review under section 39B of the Judiciary Act 1903 is limited to where:
- an assessment is tentative or provisional; or
- where conscious maladministration by the Commissioner has occurred.
There were no allegations of tentativeness or bad faith of the Commissioner amounting to maladministration by the taxpayer in Hii No. 1; the taxpayer’s counsel instead sought to establish that the principles from Futuris did not apply to the taxpayer.
The taxpayer did not succeed. The Federal Courts in Hii No. 1 and in Hii No. 2 applied the principles from Futuris and decided for the Commissioner.
Getting advice or legal help in tax disputes
It would appear that the taxpayer was selective about taking or, alternatively, following counsel. It appears that the taxpayer conducted the section 39B proceedings in Hii No. 2 from Malaysia seemingly without Australian legal representation. The Federal Court found his action in Hii No. 2 to be an abuse of process. Moreover a vexatious proceedings order was made against the taxpayer preventing the taxpayer taking further action in the court in relation to these disputes.
In contrast, through the earlier litigation, the taxpayer engaged experienced senior and other counsel. In the appeal against the objection decisions the Commissioner obtained an order for security for costs in the Federal Court against the taxpayer who is a citizen of Malaysia and who had, by then, left Australia. The taxpayer never complied with the order nor sought any extension of time to do so. One can only assume his counsel would have advised him of the risk that he would lose his rights to contest the tax bills by not engaging with the security for costs order.
The subsequent litigation shows that is what happened. The Part IVC appeal was struck out because security for costs was not given to the Commissioner. From then the taxpayer was unable to get his tax residence issue, or any review of the Commissioner’s decisions to treat him as a resident, before the courts at all despite his numerous and expensive efforts to do so.
Commissioner’s residency findings
As stated the courts were never able to get to the residence issue in the litigation. In the transcript of the High Court refusing an extension of time to apply to the High Court to the taxpayer the Commissioner’s findings of fact about the taxpayer nonetheless appear:
(i) the plaintiff was granted a permanent residency visa on 20 March 1992;
(ii) the plaintiff was granted a five year resident return visa on 27 February 1995, which allows current or former Australian permanent residents to re-enter Australia after travelling overseas and to maintain status as a permanent resident on return to Australia;
(iii) the plaintiff was issued a Queensland Drivers Licence on 6 February 1996, and his most recent Queensland Drivers Licence had effective dates of 23 December 2005 to 30 January 2011, with a Queensland address listed by the plaintiff;
(iv) the plaintiff applied on 6 September 2005 to alter his credit card limit with the National Australia Bank, listing the same Queensland address for his contact details;
(v) the plaintiff and his wife purchased the property at that Queensland address on 2 April 2001 for $6.5 million and more than six gigabytes of documents pertaining to the plaintiff’s business interests were found at that Queensland address and another property owned by companies controlled by the plaintiff;
(vi) the plaintiff’s immediate family, his wife and six children, resided in Australia as permanent residents of Australia, the plaintiff’s extended family lived in Brisbane, and his brothers lived in Victoria;
(vii) all the plaintiff’s children undertook their schooling at Queensland schools, and several children attended the University of Queensland and Queensland University of Technology; (viii) the plaintiff held in his own name 15 separate Australian bank accounts in the relevant years;
(ix) the plaintiff stayed at seven different hotels between 2002 and 2007 on his visits to Malaysia, but there was no evidence of any hotel stays when he was in Brisbane;
(x) As at 21 January 2009, the plaintiff had a number of vehicles registered to him or his wife in Australia for which insurance was obtained listing either him or his wife, or both, as the main driver, including a Lamborghini Murcielago, a Rolls Royce Phantom, a Ferrari Coupe, and a Bentley Continental;
(xi) in the relevant years, the plaintiff departed Australia 85 times, of which 84 departure cards were located on each of which the plaintiff indicated that he was an “Australian resident departing temporarily”;
(xii) the plaintiff spent between 65 and 189 days in Australia in each of the relevant years with 6 to 125 in Malaysia for the years known;
(xiii) the plaintiff was a director of seven Australian companies with registered offices in Queensland (in six of which the plaintiff held between 35% and 90% of the shares) during the relevant income years; and
(xiv) the plaintiff wrote a letter dated 12 March 2009 to the Australian Department of Immigration which he signed on behalf of one of the companies in which he was a director, which included his statement that “My family currently resides permanently in Brisbane since our first landing in 1993 … Due to the nature of my business I am forced to regularly travel overseas, because of other business interests”.
Did the taxpayer get advice about tax residency?
If these findings are plausible then, without even expressing a view on whether the Commissioner should have determined that the taxpayer was a tax resident of Australia as no Australian tribunal or court did, it can be inferred that the taxpayer was desultory in either taking or, if he took it, following advice on how to avoid being treated by the Commissioner as a tax resident of Australia.
A journalist’s report https://is.gd/KWH9jj suggests that the taxpayer may have over relied on the 183 day test (in the definition of “resident” or “resident of Australia” in sub-section 6(1) of the ITAA1936) but that report is unconfirmed. Could it be that the taxpayer did not take advice during the relevant years about the risks of his activities and circumstances possibly leading to him being treated as a tax resident of Australia either:
- under ordinary concepts?; or
- due to adopting Australia as a domicile of choice?
(See our blog from February 2020 When 183 days is not enough to make you an Australian tax resident )
It is through the relevant years in particular that advice or legal assistance to the taxpayer acted on by the taxpayer may have really counted.
Evasion and the resident determination
A further grievance of the taxpayer in the litigation was that in those years of the relevant years where the Commissioner raised original assessments based on the taxpayer’s non-resident returns, the Commissioner was out of time to amend the assessments raised under section 170 of the ITAA 1936.
Amended assessments were there raised by the Commissioner on a footing of evasion under Item 5 of sub-section 170(1).
Is getting tax residence wrong evasion?
One would think that an error by a taxpayer on the frequently nuanced and complex question of whether or not the taxpayer is a resident of Australia does not amount to evasion. However once the question of tax residence is investigated under audit by the Commissioner it is then more awkward to hide behind that simple proposition. In Hii No. 1 it is stated that the Commissioner justified his evasion determination on the following acts of the taxpayer:
a. Listing a Singapore business address on his Australian tax return as his residential address
b. Providing different reasons as to why various addresses are used in each country [during the course of the audit]
c. Not providing details of his offshore income and assets when requested [during the course of the audit]
d. Failing to provide full and complete details of foreign entities he controls [during the course of the audit]
e. Omitting foreign source income from his Australian tax returns; and
f. Failing to pay appropriate tax in Australia.
(see paragraphs 12 and 28)
Viewed skeptically one could suggest that facts e. and f. could happen when a taxpayer innocently believes they are a tax non-resident and may not be evasion. Facts a. to b. more strongly can support an evasion finding.
Evasion & co-operating with an audit
From c. and d. it can be inferred that full co-operation with the Commissioner in the course of an audit is an imperative where a taxpayer is contesting an amended assessment which would be out of time in the absence of fraud or evasion.
The question again arises, did the taxpayer get or follow advice this time about what information to provide to the Commissioner’s auditors? Based on c. and d. the withholding of information from the auditors prejudiced the taxpayer’s position on the evasion issue.